Personal Mobile & eBanking Access Issues
We’re aware of an issue affecting access to Exchange OnLine and Personal Mobile Banking for some customers. Our team is working to restore full service as quickly as possible. We appreciate your patience.
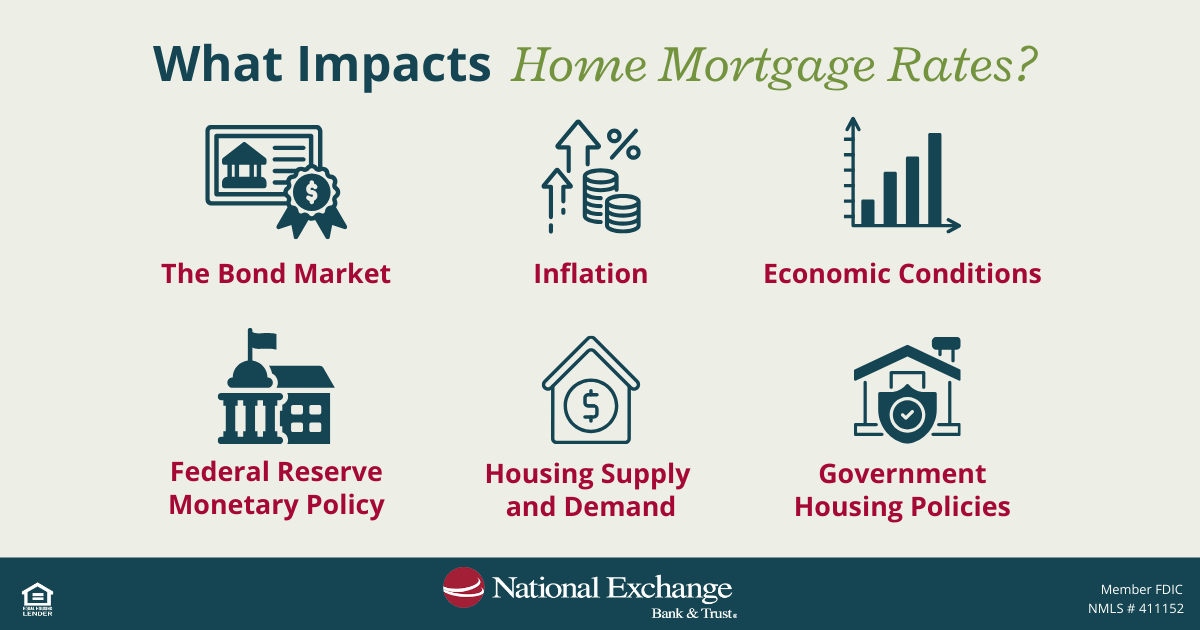
Mortgage rates are influenced by a combination of economic conditions, government policy and market demand. With the Federal Reserve cutting interest rates three times in 2025, many homebuyers and homeowners are wondering what’s going on with mortgage rates.
While Fed rate changes often make headlines, mortgage rates are not controlled by a single factor. In this guide, we’ll break down the key factors on what impacts mortgage rates, so you can better understand why rates rise and fall and what that means for your home financing decisions.
The prime rate is the interest rate banks offer to their most creditworthy customers. It is influenced by the Federal Reserve and directly impacts variable-rate consumer loans such as credit cards and home equity lines of credit (HELOCs).
However, the prime rate does not directly affect long-term fixed mortgage rates, such as 15- or 30-year fixed mortgages. Instead, fixed mortgage rates are driven by broader, long-term economic indicators, particularly inflation and government bond yields.
Major economic impacts that affect fixed rates (such as mortgages) are government treasury bonds, treasury bills, other long-term government investments, the stock market and inflation. In addition to this, our local mortgage lenders keep a close eye on various government policies as well as supply and demand to have an idea of where rates are headed.
The Federal Reserve influences interest rates by adjusting short-term rates to help control inflation and stabilize the economy. When the Fed raises rates to curb inflation, mortgage rates often increase as borrowing becomes more expensive. Conversely, when the Fed lowers rates, mortgage rates may decrease but not always immediately.
Mortgage rates often reflect expectations about future Fed actions, meaning changes can occur before official rate announcements.
Inflation is one of the most significant drivers of mortgage rates. When inflation rises, lenders demand higher interest rates to protect the future value of their returns.
Mortgage rates also closely track yields on long-term government investments, such as U.S. Treasury bonds and Treasury bills. As bond yields rise, mortgage rates typically increase; when bond yields fall, mortgage rates often follow.
A strong economy with low unemployment rates can push interest rates up due to increased demand for loans. In general, when there is a high demand for mortgages, the mortgage market may increase rates to help find balance between supply and demand. On the flip side, when there is an abundance of homes for sale, and the demand for mortgages is lower, this can lead to lower mortgage rates to help attract new home buyers.
Various government housing and tax policies can also influence mortgage rates. Housing policies could include changes to FHA, VA, and USDA loans. When more lenient credit requirements are offered, homeownership is more accessible. In the same token, stricter eligibility criteria can impact mortgage rates and availability. Additionally, first-time homebuyer tax credits will increase demand for housing, thus increasing rates, which goes back to the point on supply and demand.
While market conditions influence mortgage rates, borrowers can take steps to improve their individual rate.
If you’ve been keeping your eye on mortgage rates for some time, you know they can change in an instant. To stay up to date NEBAT recommends connecting with a local mortgage lender to help guide you through financial decisions having to do with your mortgage.
The NEBAT Home Loan App also provides a wealth of information in the palm of your hands.
Find Your Local Lender Download on Google Play Download on the App Store
Not directly. The government, including the Federal Reserve, influences short-term interest rates and economic policy, but long-term mortgage rates are primarily determined by market forces such as inflation, Treasury bond yields, housing supply and demand, and investor activity. Government programs like FHA, VA, or USDA loans can affect borrower access and demand, which can indirectly impact rates.
Mortgage rates can change daily, and in some cases multiple times per day, based on market conditions, economic data and investor activity. Rates are not guaranteed until they are locked in.
Yes, mortgage rates can sometimes be negotiated. Rates may vary by lender, loan type, credit profile and market conditions. Improving your credit score, increasing your down payment, comparing multiple lenders, or asking about discount points can help you secure a better rate.